VQE for delivering good audio quality
The prolonged COVID-19 pandemic has led to a significant increase in non-face-to-face activities, such as remote working and distance learning. As people continue to adapt to the new normal, many have realized the advantages of these activities and have come to prefer them. Even as the pandemic subsides, the trend towards non-face-to-face activities has been growing steadily.
For non-face-to-face activities, it is essential to have a video conferencing system that allows participants to convey information to one another. This article explores how voice information is delivered in a video conference and explains how to deliver voice with better quality.
In this article, you can find guidance on how to improve the surrounding environment during a video conference and understand how LINE Planet's Voice Quality Enhancement (VQE) filter can enhance audio quality. You will also learn how to adjust VQE to improve audio quality in different situations.
Importance of audio quality
Voice information is the most fundamental means of human communication, and it is particularly important in non-face-to-face activities such as video conferencing. In a video conference, a voice is transmitted to all participants, so poor audio quality can cause fatigue for the other users. For instance, background noise or echoes can make it challenging for others to comprehend what you are saying or to concentrate on the conversation. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that good quality voice is delivered for a smooth meeting.
There are two approaches to improving voice quality. The first involves making changes to the surrounding environment to minimize noise and other disturbances, while the second involves using voice filters such as VQE. This article examines both approaches.
Setting up user environments to enhance voice quality
To understand how to set up user environments in order to enhance voice quality, it's necessary to examine the speech transmission process and the factors that affect audio quality.
Speech transmission process and quality factors
Understanding how a voice is transmitted can help you identify the factors that contribute to audio quality. The process by which a voice is transmitted to other participants in a video conferencing system is as follows:
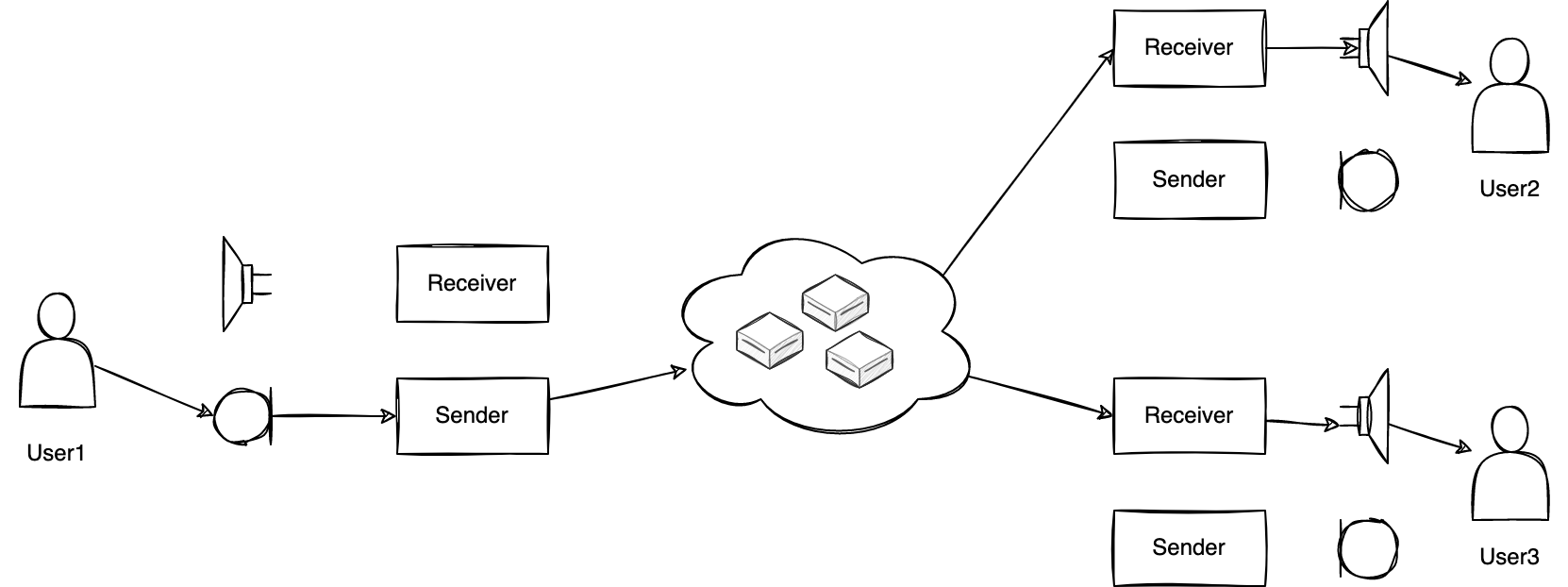
The voice of a talker (User1) is transmitted to the microphone in the form of air vibrations, and the microphone converts it into a digital signal. The digital signal is compressed at the sender and delivered to other participants (User2, User3) in packet form through the server. The packets are decoded by the receiver and output to the speaker. Through this process, the participants can hear the voice information of the talker.
A microphone is a device that converts air vibrations into digital form, so it picks up all sounds generated around it. Most of the sounds other than a voice in the picked up sounds are unnecessary. If those sounds are transmitted along with the voice, they will disrupt the voice information and distract other participants from the meeting. Additionally, voice quality may be degraded depending on the network condition.
Therefore, we can see that the performance of the audio device, the surrounding environment, and the network condition affect the voice quality. Among these factors, only the audio device and surrounding environment factors will be covered in this article. Regarding each factor, we will look at how we can improve noise, echo, inadequate loudness, and howling, which are typical factors that negatively impact the delivery of voice information.
Audio device factors
Let's look at the factors of the audio device that can negatively impact the delivery of voice information and how to mitigate them.
Noise
Audio devices themselves can generate noise in various forms and by various causes. Poor contact of the microphone jack, grounding issues, and electrical noise from low-quality microphones are among the main causes.
This type of noise tends to occur in low-quality microphones with a low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). To reduce this type of noise, it's best to avoid using low-quality microphones.
Loudness
Your voice is the most important information in a video conference, so it's crucial for your voice to be heard clearly above all else. If your voice is too low or too loud, it can cause fatigue for other participants in the meeting.
Difference in voice volume levels can occur due to various factors, but the main reason is difference in audio levels picked up by the microphone. This depends on the microphone's pickup characteristics, which may vary depending on the sensitivity or performance of the microphone itself. In particular, directional microphones can have different sound pickup levels based on the direction of the microphone. Differences in loudness may arise based on the distance between the talker and the microphone or the intensity of the vocalization. In general, it's recommended to keep the distance between the microphone and the mouth within the range of 5 cm to 100 cm.
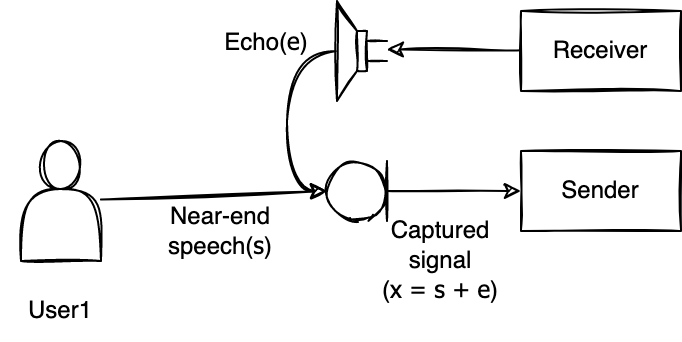
Echo
When the other user's sound is output to your speaker, it is also picked up by your microphone. An echo occurs when sound is reflected by a medium and returns back. The microphone, which transmits the picked up sound, can be regarded as the main source of echo.
If the other user's sound is picked up and transmitted through your microphone, they will hear their own sound again with a time difference. This can cause inconvenience for all participants in the video conference.
The source of the echo is the speaker. The echo level increases as the distance between the microphone and the speaker gets closer, the speaker output gets louder, and the microphone sensitivity gets higher. Therefore, keeping the distance between the speaker and the microphone as far as possible and not raising the speaker output level and the microphone input level too much will help reduce the echo level.
Using an audio device that combines a speaker and microphone can also help improve the voice quality. In particular, when an earset or headset is used, the echo level is very small because the sound output from the speaker is transmitted directly to the ear and blocked from the outside. Additionally, since the voice is picked up at a close distance from the mouth, noise sources can be minimized due to the high SNR.
Surrounding environment factors
Let's look at some factors that can negatively impact the delivery of voice information in the surrounding environment and how to mitigate them.
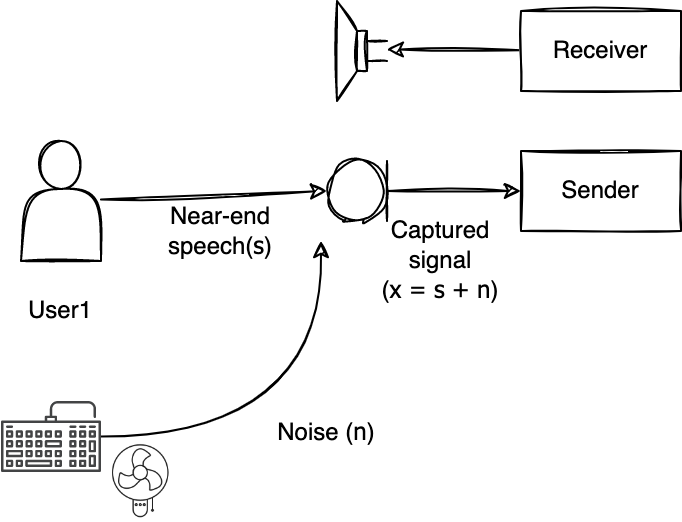
Noise
The microphone captures vibrations in the air as sound, so it can also pick up any background noise. This may include the sound of a computer fan, keyboard typing, or an electric fan. Therefore, it is recommended to position the microphone as far away from noise sources as possible.
Even minor vibrations can create significant noise if the distance from the microphone is short. If you're making a call in a noisy environment like a café, construction site, or roadside, it's best to keep the microphone muted and unmute it only when you're speaking to reduce noise-related inconvenience.
Howling
Howling is a feedback loop phenomenon that occurs when sound output from the speaker is picked up as the microphone input and amplified continuously, creating noise. Howling can occur when multiple devices are used to participate in a meeting in the same room. To avoid this, mute the microphones of all devices or leave one device unmuted while muting both the microphones and speakers of the other devices.
Summary of methods for improving environments
You can use the following methods to improve your environments to deliver voice in better quality.
| Environmental factors | Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Audio device factors | Noise | Avoid using low-quality microphones |
| Loudness | Keep a distance of 5-100 cm from the microphone | |
| Echo | Using earsets or headsets | |
| Surrounding environment factors | Noise | Remove noise sources from the microphone. Use mute. |
| Howling | Use only one device in one space |
Case of improving factors that interfere with voice quality
Here's an example of improving voice quality by addressing the factors discussed above.
Once a user who was attending a video conference held in a large venue (indoor auditorium) reported that the voice quality of the presenter in the venue was poor. The venue environment was as shown in the following figure.
The presenter used a handheld room microphone, and the presenter's voice was transmitted to the audience through the room speakers connected to the room microphone. Additionally, a laptop was placed between the presenter and the room speakers, and the laptop camera and microphone were connected to the video conference to stream the presentation in real time.
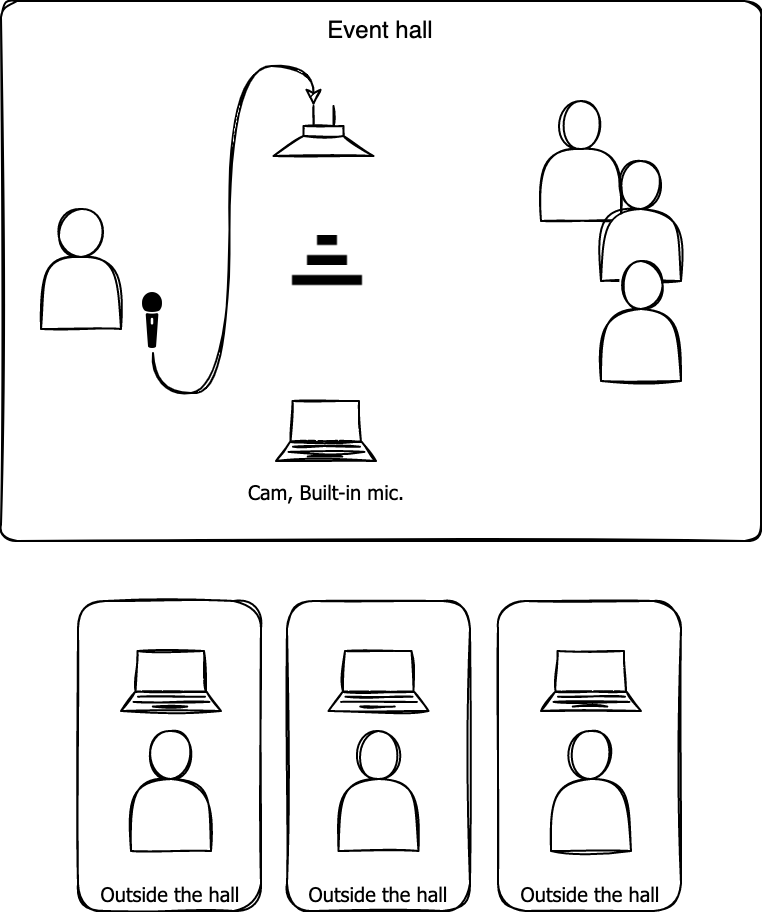
The audio path between the presenter and the laptop's built-in microphone is as follows: presenter → room microphone → room speakers → laptop's built-in microphone. The longer the audio path, the more likely it is to increase latency and degrade audio quality. There are two main problems with setting up the audio path like this.
- The distance between the room speakers and the laptop's built-in microphone is long, so the presenter's voice received by the laptop's built-in microphone becomes low, and noise from around the venue is picked up, resulting in a low SNR. Moreover, since this audio path includes an analog section and an acoustic section, the audio quality is affected by the performance of the room speakers and the laptop's built-in microphone.
- The presenter's voice is picked up by the laptop's built-in microphone, echoed throughout the venue, and delivered multiple times to the video conference participants.
Due to these issues, the quality of the presenter's voice in the video conference was degraded. Achieving a high SNR is important for good voice quality. In other words, setting up an environment in which the presenter's voice is significantly louder than the surrounding background sounds will ensure good voice quality, even with outside noise.
Let's see the following figure.
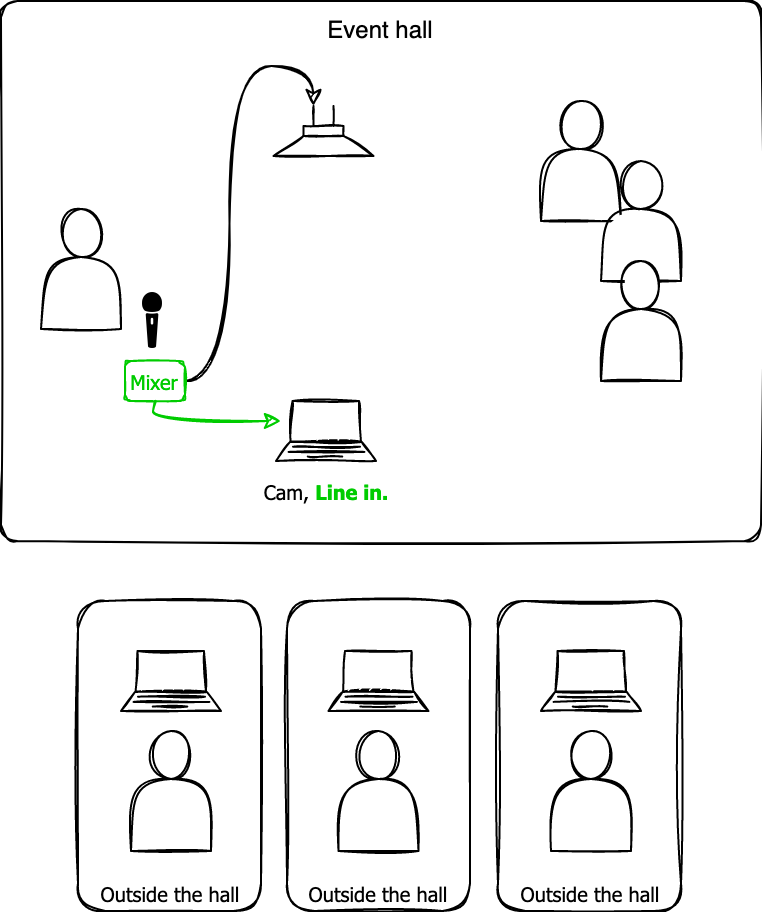
In this setup, a mixer is connected to the room microphone and its output is fed into the laptop line input. The audio path is as follows: presenter → room microphone → built-in line input. By shortening the audio path in this way, the acoustic section was removed and the part affected by the performance of the room speakers was also removed. In the analog section, the room microphone only remains. In other words, the audio received on the participant's laptop purely depends on room microphone's performance. In addition, since the distance between the room microphone and the presenter as well as the distance between the noise source and the presenter is large, a high SNR can be obtained and audio quality degradation can be significantly reduced.
VQE for LINE's excellent voice quality
As we saw in the example above, users can manually adjust the noise, loudness, and echo to improve voice quality.
However, we cannot expect users to set up perfect environments all the time. For this reason, LINE's video conferencing system provides a high-performance VQE audio filter that postprocesses the sound picked up by the microphone to enhance its quality. LINE's capability to deliver superior voice quality in calls and meetings is thanks to the VQE filter of LINE Planet, a VoIP platform built with years of research. VQE improves voice information by suppressing distracting sounds and controlling the volume of key sounds.
What is VQE?
VQE stands for "Voice Quality Enhancement" and refers to a collection of audio filters that improve voice quality. VQE mainly consists of three filters: a noise suppressor, an acoustic echo canceller, and an automatic gain control. Each filter improves the interfering factors of audio quality, such as background noise, loudness, and echo. Therefore, the VQE module is essential to improve voice quality.
VQE can be divided into built-in type and LINE Planet type. The built-in type refers to the VQE included in the audio device or the OS itself, and the LINE Planet type refers to the VQE provided by the LINE Planet platform. The built-in type has filters tuned to the characteristics of the audio device (microphone and speaker), so it generally provides better quality in the device than the LINE Planet type. On the other hand, the LINE Planet type is tuned to work universally with a variety of audio devices.
LINE Planet's VQE offers a variety of filters. In this article, we will only describe the filters that are required for calls.
Noise suppressor
A noise suppressor (NS) is a noise removal filter that classifies all signals except voice as noise and removes them.
The following figure shows the noise removal process in NS provided by LINE Planet.
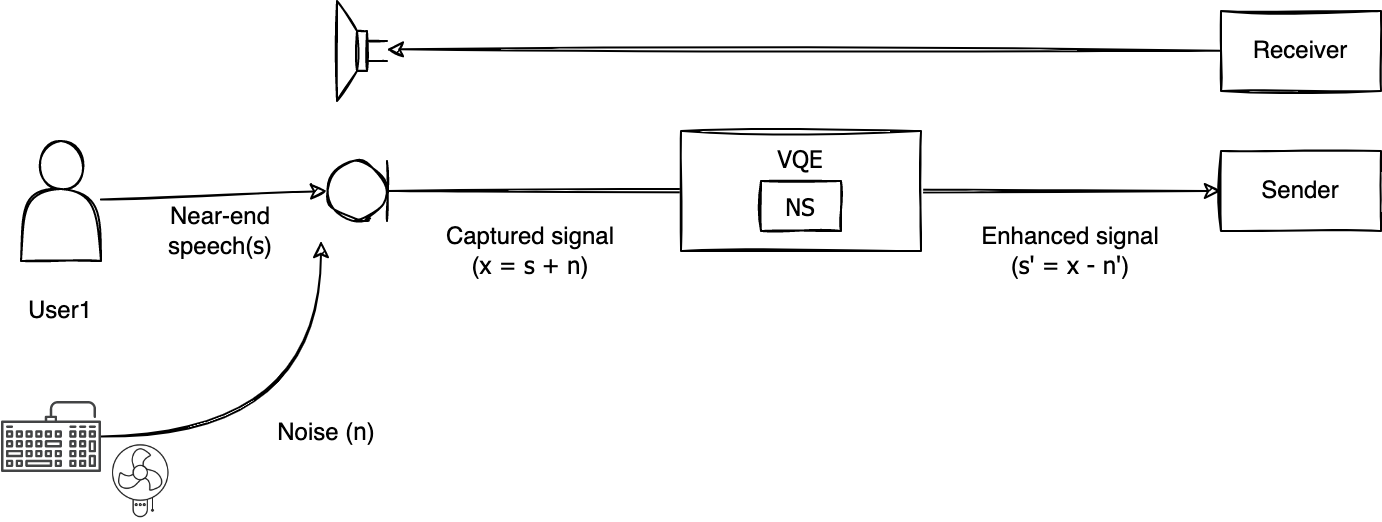
The signal x picked up by the microphone is the sum of the talker's voice s and the background noise n. NS generates n' which is an estimate of n, and subtracts n' from x, leaving only the talker's voice (s'). At this time, the performance of NS can be evaluated according to the degree to which n' is similar to n. In other words, the closer n' is to n, the closer s' is to s.
LINE Planet offers two versions of NS. One is a legacy filter for low-end devices (legacy NS), and the other is a high-performance filter (MLNS) using machine learning (ML). NS for low-end devices mainly removes stationary noise such as fan noise, while high-performance MLNS performs better because it can remove not only stationary noise but also nonstationary noise such as keyboard sound.
Acoustic echo canceller
An acoustic echo canceller (AEC) is a filter that removes only the echo from the sound picked up by the microphone. AEC receives the sound to be output to the speaker as a reference and finds and removes the echo component from the signal picked up by the microphone.
The following figure shows how AEC provided by LINE Planet removes echoes.
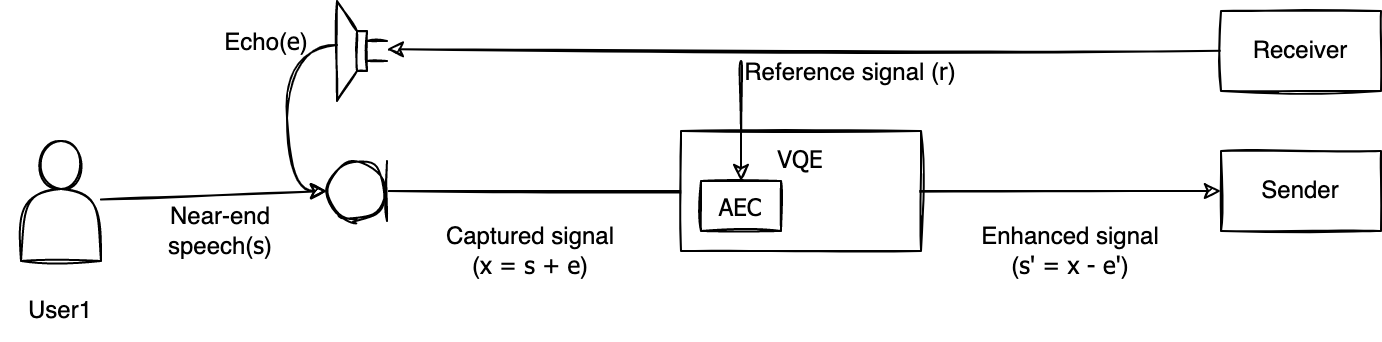
The signal x picked up by the microphone is the sum of the talker's voice s and the echo e.
AEC uses the signal r output to the speaker as a reference to create e' by estimating e from x and subtracts e' from x, leaving only the talker's voice (s'). Like NS, the performance of AEC can be evaluated according to the degree to which e' is similar to e. In other words, the closer e' is to e, the closer s' is to s.
Automatic gain control
The loudness of the voice picked up by the microphone depends on the sensitivity of the microphone and the state of the user's vocalization. An automatic gain control (AGC) is a filter that maintains fluctuating voice volumes at a constant level. That is, AGC limits the output if the signal is too loud and boosts the signal if it is too small.
LINE Planet provides two types of AGC: H/W type (H/W AGC) and S/W type (S/W AGC).
- S/W AGC compensates the volume by multiplying gain so that the volume of input voice remains at a constant level. However, the mode has limitations because too much compensation can have an adverse effect on audio quality. Better audio quality can be guaranteed when a suitable volume is input from the microphone. The hardware mode is used for this purpose.
- H/W AGC controls the volume by calculating the energy of speech section in the signal
xcoming from the microphone. If it is greater than the reference level range, the microphone sensitivity is reduced. If it is less than the reference level range, the microphone sensitivity is increased. If it is within in the reference level range, the microphone sensitivity is maintained so that the voice comes in at a constant level. Since H/W AGC directly controls the microphone device, it is provided only for platforms that can control the microphone, such as Windows and macOS.
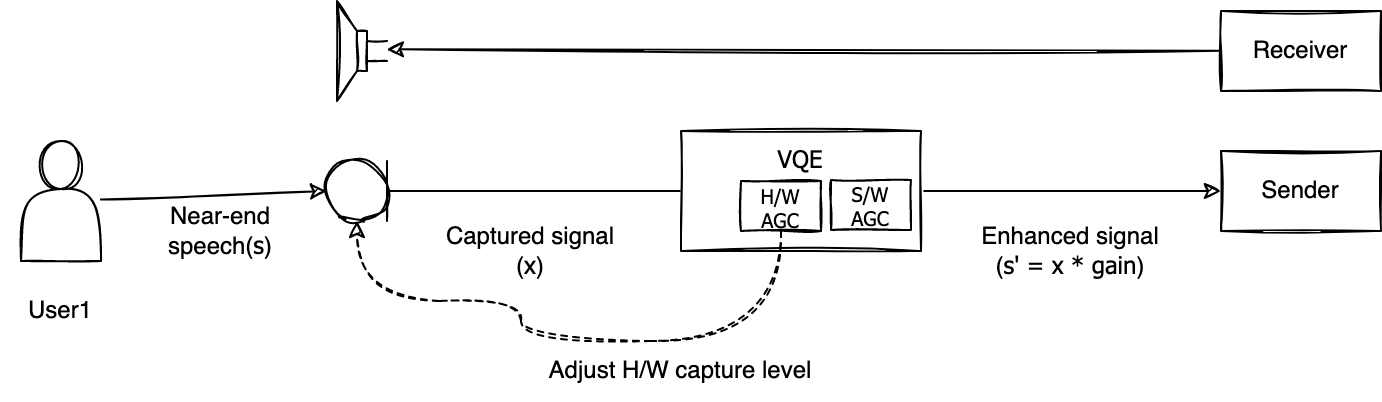
The following figure shows how H/W AGC provided by LINE Planet works. After the microphone sensitivity is adjusted using H/W AGC, the volume is compensated once more through S/W AGC.
VQE filter control
In general, using a VQE filter helps improve audio quality, but there are times when it may not be helpful depending on the device used or the situation. To prepare for this, LINE Planet provides the feature to turn the VQE filter off or on.
So when is it good to turn each filter off? Let's look at situations where controlling audio filters using the VQE control API can improve audio quality.
Cases when it is better to turn off the VQE filter
When using an audio device with built-in AEC
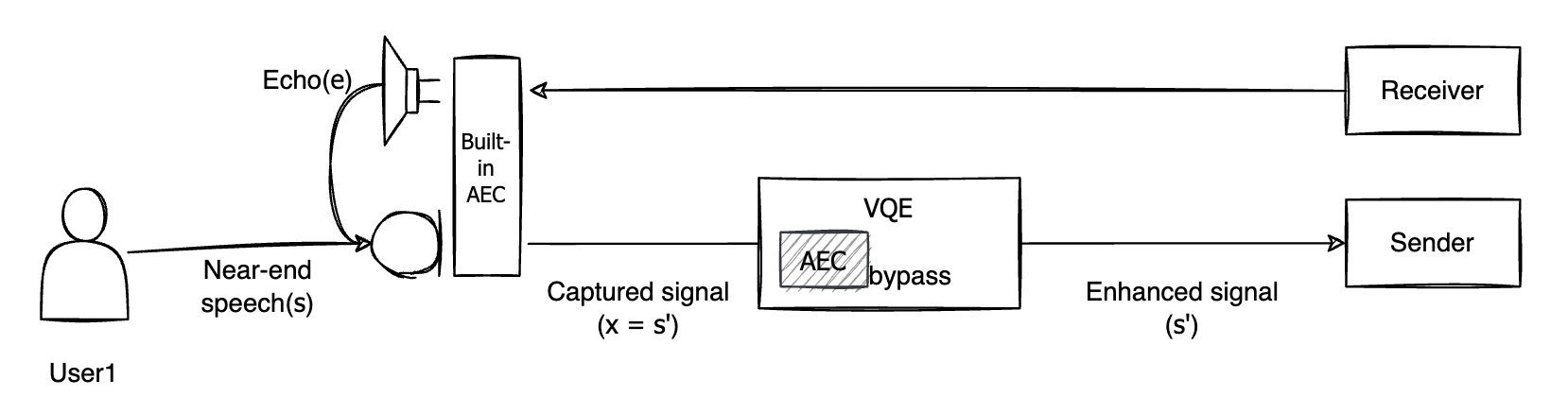
High-performance devices, which are often equipped with a microphone and speakers in one audio device, often provide built-in AEC. The built-in AEC is tuned to the characteristics of the audio device, so it usually outperforms LINE Planet's AEC.
With AEC, near-end speech may be distorted in the process of canceling the echo e from the signal x picked up by the microphone. In devices with built-in AEC enabled, the echo has already been canceled through the built-in AEC, so passing through LINE Planet AEC again may only increase distortion. Therefore, for audio devices with built-in AEC enabled, turning off LINE Planet AEC and bypassing the picked up signals can help improve audio quality. If the built-in AEC doesn't cancel the echo sufficiently, turning on LINE Planet AEC to remove the remaining echo may help.
On iOS, built-in AEC works by default, so LINE Planet AEC is turned off by default.
The following figure shows how audio is processed on an audio device with built-in AEC when LINE Planet's AEC is turned off.
When playing an instrument or transmitting music
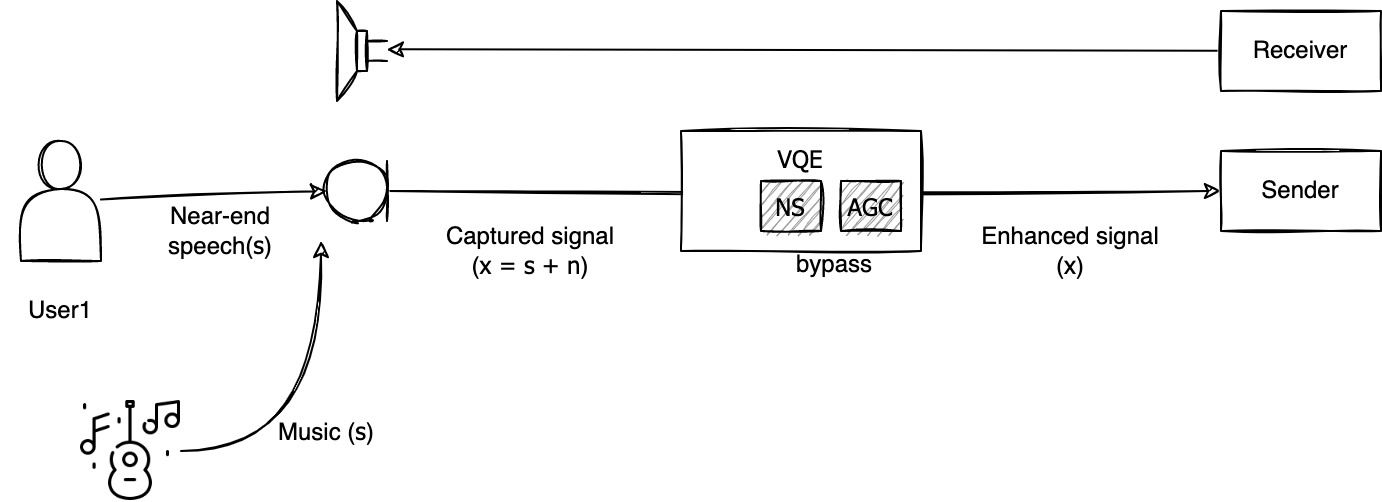
NS classifies signals other than voice as noise and removes them from the picked up signals. Music is also classified as noise, so it is subject to removal by NS. If you want to transmit musical instrument playing or music playback in a video conferencing system, it is recommended to turn off LINE Planet's NS. However, when LINE Planet NS is turned off, not only music but also background noise is transmitted, making it even more important for users to reduce noise sources as much as possible.
On audio devices equipped with built-in NS, music signals may already be classified as noise and removed before being input to LINE Planet. In this case, even if you turn off LINE Planet's NS, the effect may not be significant. For example, in iOS or Android, the built-in NS works by default, so it is difficult to guarantee good quality if the music signal is transmitted through the microphone.
AGC controls the volume. Since music signals are also subject to volume control, it is recommended to turn off LINE Planet's AGC if you want to deliver music signals where dynamics are important. However, turning off LINE Planet's AGC means that the volume is not compensated, so it becomes even more important to adjust the microphone sensitivity and the distance between the microphone and the sound source to ensure that the appropriate volume reaches the microphone.
The following figure shows how audio is processed when LINE Planet's NS and AGC are turned off.
VQE control API
As mentioned before, LINE Planet provides APIs for video conferencing software developers to control LINE Planet's NS, AEC, and AGC.
Using this API, you can turn VQE on or off, or adjust individual filters.
For more information on LINE Planet's VQE control API, see VQE control.
The VQE control API is supported by PlanetKit 4.3 or higher.
VQE audio filter default values by platform
There may be some other settings depending on the type of audio device or mobile device, but the basic settings used by LINE Planet are shown in the following table.
| Platform | AEC | NS | AGC type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Android | RECOMMENDED | ENABLED | SOFTWARE (HARDWARE mode unsupported) |
| iOS | DISABLED | ENABLED | SOFTWARE (HARDWARE mode unsupported) |
| macOS | RECOMMENDED | ENABLED | HARDWARE |
| Windows | RECOMMENDED | ENABLED | - PlanetKit 4.3 and 4.4: SOFTWARE - PlanetKit 5.0 or higher: HARDWARE |
Future direction of VQE filter improvement
LINE Planet applied machine learning technology to NS to significantly improve noise removal performance in video conferences. In the past, NS could mainly remove stationary noise such as fan noise, but machine learning-based NS can remove all noise except voice. However, it is currently only available for Windows and macOS because of the high computational load compared to the legacy NS. Since the amount of computation is being greatly reduced through optimization, it will be applied to mobile platforms soon.
The LINE Planet team is also developing AEC using machine learning to improve not only echo cancellation performance but also audio quality in double-talk situations. The machine learning-based AEC is also planned to be applied to the desktop platforms first and then applied to the mobile platforms after optimization.
In addition, when a person continuously listens to sound with a certain tone, fatigue accumulates and concentration decreases during video conferences or remote classes. The LINE Planet team is also researching methods to reduce fatigue by adding spatiality to the received voice.
Conclusion
Because of the wide variety of audio devices and different forms and purposes of using video conferencing systems, it is very difficult to provide good quality in all situations, all the time. The LINE Planet team is continuously performing research and development, adding features and improving performance to provide voice quality that is more suitable for each situation. We hope that more users will be able to enjoy optimal audio quality in the future.